Ashford Clinic Blog
What are Parathyroid Glands?
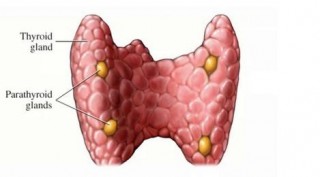
Thyroid...parathyroid...probably the same thing, right? Not at all! These glands serve two very different purposes. While the thyroid is responsible for regulating metabolism (among other things), the parathyroid glands regulate and maintain calcium levels in the blood. Though their names are very similar, the thyroid and parathyroid actually have very little in common aside from their location and the fact that both are part of the endocrine system. Here are some important things you should know about your parathyroid glands.
Everyone has an average of four of these peasized glands tucked around the thyroid gland. They secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which causes calcium to be reabsorbed into the kidneys as well as released from bone. As blood filters through, the amount of calcium present in the blood is detected and the glands react by producing more or less PTH. The parathyroid glands are constantly monitoring and reacting to calcium levels in the blood, thus maintaining a very narrow “normal” range of calcium.
Keeping the amount of calcium in the blood at a normal level is essential to life, as calcium serves three important purposes in the human body:
- Providing electrical energy for the nervous system
- Providing electrical energy for the muscular system
- Providing strength to the skeletal system
In fact, calcium is the only element or mineral with its own regulatory system in the human body.
Sometimes, these glands become problematic by functioning on their own with no regard for what is going on in the rest of the body. When this occurs, more PTH than usual is released calcium levels increase above the normal level. This is referred to as hyperparathyroidism, which causes hypercalcemia (high calcium levels). Symptoms of hypercalcemia can include kidney stones, osteoporosis or loss of bone density, bone fractures and/or bone pain, abdominal discomfort including pancreatitis, nausea, and constipation, muscle discomfort, muscle weakness, joint pain, memory loss, confusion, fatigue, and depression. Because the symptoms are quite vague and can be attributed to a number of causes, diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism often occurs when routine blood work shows hypercalcemia.
Treatment for hyperparathyroidism is surgical removal of the abnormal parathyroid gland through a small incision in the neck. Once the abnormal gland is removed, hormone levels return to normal, which also causes calcium levels to return to normal. If you think you are suffering from hyperparathyroidism, contact your doctor to determine the best course of action for you. If you are in the Athens, GA area, the Ashford Clinic is here to help!


